CORS (Everyone’s Favorite!), MVC and Nginx
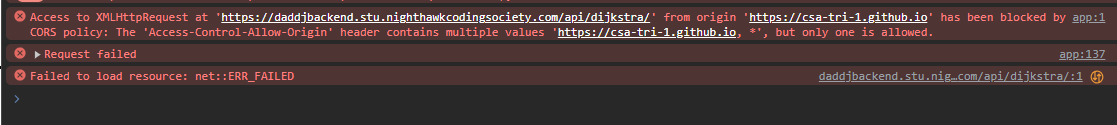
What is CORS and what does it actually do?
- CORS stands for __ __ Resource Sharing and it works to defend the the server side (APIs and the Backend)
- When you make a request on the client side (the frontend site), your sending a request to another site which has an API, CORS works to protect sensitive data and make sure that only ___ websites and the site with the server to have access to the data.
Where can you find CORS and how can you modify it and add it to your site?
If you go to any backend server you git cloned from Mr.Mort’s spring_portfolio, if you go ahead and navigate to SecurityConfig.java under /src/main/java/com/nighthawk/spring_portfolio/ and scroll down, you see the following the code:
.cors(Customizer.withDefaults())
.headers(headers -> headers
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true"))
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-ExposedHeaders", "*", "Authorization"))
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type", "Authorization", "x-csrf-token"))
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-MaxAge", "600"))
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "POST", "GET", "OPTIONS", "HEAD"))
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://link1", "http://link2", "http://link3", "http://link4"))
What this is showing is the different things that a request must include in order for a request from a site to go through
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true")):
- This header indicates whether the __ should include credentials (like cookies, HTTP authentication, and client-side SSL certificates) in the request
- This is typically used when the server needs to send and receive cookies on the requested domain.
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-ExposedHeaders", "*", "Authorization")):
- This header, enables you to specify __ headers (“*”) and grants the browser to expose headers like “Authorization” to the client.
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type", "Authorization", "x-csrf-token")):
- This line is listing the headers that the client is allowed to use in the actual request
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-MaxAge", "600")):
- This line specifies that the results of a ___ request can be cached for in this case, 600 seconds
- What this does in other words is before the actual request is received, a small request is typically sent and this request is saved for 600 seconds allowing for it so when similar calls are made, the result of the initial call is reused, this improves the performance and latency.
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "POST", "GET", "OPTIONS", "HEAD")):
- This line just lists the different HTTP methods that are allowed when making a request
.addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://link1", "http://link2", "http://link3", "http://link4")):
- This line simply specifies what links are allowed to make requests to the server
Frontend Side of CORS
- Based on the headers you assigned in the backend, your frontend fetch request must match what you defined
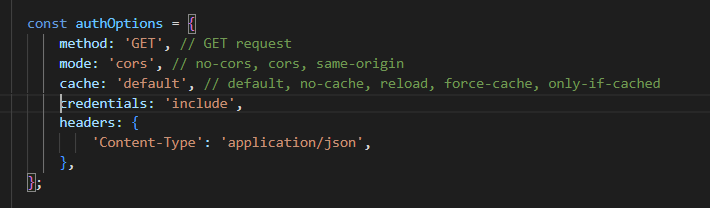
Some key reminders:
- When working with an API on the backend, in the areas where you want to protect the data, don’t forget to do
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;and include@CrossOriginbefore the actual code
MVC and Nginx
MVC
- MVC stands for ___ View Controller, and its purpose is to build user interfaces and web applications and divides the application into three interconnected components: Model, View, and Controller
Model:
- The model is responsible for managing data and the logic and rules for manipulating the data
- It is ___ from the user interface and works with the View and Controller
View:
- The view is the part that works and is responsible for receiving the user input and presenting the data to the user
- It receives ___ from the Model and sends the user input to the Controller
Controller:
- The controller functions to update the Model and sends the updates to the View
- It makes and handles the decisions that the user makes, updating the Model and View to adapt to it
A great example of the MVC system would be the PersonAPI on the spring_portfolio, where the Person.java is the Model, PersonDetailsService.java is the View, and the PersonAPIController.java is the controller
MVC functions:
- MVC serves in order to make the code separated into different roles and parts allowing for it to be easily ___ and easily reusable. It also provides great extendability and makes it really easy to test the code since each part is essentially independent from each other.
Nginx
Nginx is a web server and reverse proxy server that has a wide variety of functions that enable for better performance, security, and connections between a client and the server. Some its most important features include:
- Web Server
- Nginx is able to handle incoming HTTP and HTTP requests from the client side with high performance, and can enable for the the direct serving of __ content to the client side
- This enables for really efficient delivery of static resources to the web applications
- Reverse Proxy
- Nginx is a reverse proxy server as well and what this means is it takes requests from the frontend and connects it with the backend server and takes the response from the server and sends it back to the frontend
- This serves to shield the backend from being exposed to the internet and also enables many frontend clients to ___ with the backend
- Balancing Loads
- Nginx also helps to distribute the incoming requests and traffic equally among the backend servers and as a result, prevents the backend from being overwhelmed
- As a result, this significantly helps the performance and the maintenance of the backend server and enables for efficient communications
- SSL/TLS Termination:
- Nginx also can __ and __ the incoming data, from the frontend, sending it to the backend server
- This functions as a way to both ensure secure communications and also serves as a process to make the backend focus on running ___ instead of attempting to understand the request
